While presenting, I felt that our TED talk went fine, but now that I am reflecting on it, there were many places we could have fixed things. I realize now that our topic and our goal became too general and there was not a clear path and point to be made. Because of our broad topic, our presentation dragged for too long. I feel that we deserve the grade we received and could have worked harder to narrow down our topic. Next time I do a project like this that does not set clear guidelines I will remember to make sure I have a clear end goal because there are so many things that can cause progress to go off track.
Tuesday, May 31, 2016
20 Time Final Post
While presenting, I felt that our TED talk went fine, but now that I am reflecting on it, there were many places we could have fixed things. I realize now that our topic and our goal became too general and there was not a clear path and point to be made. Because of our broad topic, our presentation dragged for too long. I feel that we deserve the grade we received and could have worked harder to narrow down our topic. Next time I do a project like this that does not set clear guidelines I will remember to make sure I have a clear end goal because there are so many things that can cause progress to go off track.
Tuesday, May 10, 2016
Reflexes Lab
In this lab we tested our responses to certain stimuli and investigated why we had these reactions. This activity relates back to our unit in that it deals with reflexes. Reflexes are rapid, predictable, and involuntary responses to stimuli. There are somatic reflexes, which stimulate skeletal muscles, and autonomic reflexes, which regulate smooth muscle and other automatic responses.
1. In the photopupillary reflex test the reflex of the pupil dilated and shrinking was being tested. In the test the pupil shrunk when exposed to light after being the dark after a certain amount of time. This reflex occurred because the pupil changes size with the amount of light that is present, so with more light it will decrease in size and vice versa.
2. In the knee jerk reflex test the reflex that was being tested was the knee-jerk reflex which is when the knee jerks upward when the knee cap is hit. The arc is a 2 neuron reflex arc where the sensory neuron sends a signal to the spinal cord then travels to the motor neuron then the knee. In the test my knee did jerk upward ,and after doing squats, the reflex actually increased in intensity when it was not supposed to because the reflex is supposed to slow down after exercise due to the decrease in ATP. This probably resulted in the fact that I did not do enough squats.
3. In the blink reflex test the person is supposed to blink when the cotton ball is thrown at them. This occurred during the test. This reflex exists in order for humans to protect the eye from anything that can potentially damage it because it is very sensitive as well as important part.
4. In the plantar reflex test the toes are supposed to curl when the pen is moved across the bottom of the foot. This was apparent during the test when the toes curled inward when he pen moved across. This response occurred because the toes react in a way that makes the foot want to move away from that source of touch in order to protect the foot.
5. In the response time test our time was recorded in catching a ruler that we saw falling through our finger tips and then recorded again while texting. After the trials were complete, I saw that my average time went from 0.15 seconds to 0.7 seconds. There was a significantly slower time while texting. This change is due to the fact that the brain takes time to select what action is prioritized ,and texting can slow down the response time, showing the dangers of texting and driving
1. In the photopupillary reflex test the reflex of the pupil dilated and shrinking was being tested. In the test the pupil shrunk when exposed to light after being the dark after a certain amount of time. This reflex occurred because the pupil changes size with the amount of light that is present, so with more light it will decrease in size and vice versa.
2. In the knee jerk reflex test the reflex that was being tested was the knee-jerk reflex which is when the knee jerks upward when the knee cap is hit. The arc is a 2 neuron reflex arc where the sensory neuron sends a signal to the spinal cord then travels to the motor neuron then the knee. In the test my knee did jerk upward ,and after doing squats, the reflex actually increased in intensity when it was not supposed to because the reflex is supposed to slow down after exercise due to the decrease in ATP. This probably resulted in the fact that I did not do enough squats.
3. In the blink reflex test the person is supposed to blink when the cotton ball is thrown at them. This occurred during the test. This reflex exists in order for humans to protect the eye from anything that can potentially damage it because it is very sensitive as well as important part.
4. In the plantar reflex test the toes are supposed to curl when the pen is moved across the bottom of the foot. This was apparent during the test when the toes curled inward when he pen moved across. This response occurred because the toes react in a way that makes the foot want to move away from that source of touch in order to protect the foot.
5. In the response time test our time was recorded in catching a ruler that we saw falling through our finger tips and then recorded again while texting. After the trials were complete, I saw that my average time went from 0.15 seconds to 0.7 seconds. There was a significantly slower time while texting. This change is due to the fact that the brain takes time to select what action is prioritized ,and texting can slow down the response time, showing the dangers of texting and driving
20 Time Individual Reflection
During this 20 time project, I learned a lot about time management and giving my time to something that interests me outside of school. I challenged myself by doing things outside my comfort zone such as picking up a musical instrument, the ukulele, and talking to new people. My initial focus was actually to learn something about how the arts could improve people's lives inside and outside of school by helping develop certain ways of thinking as well as keeping a healthy mental state. However, after working on this project, I also saw some self improvement in that I learned how to set aside time from what I normally do to pursue this project and challenge myself. While working with Michael, I planned to not only do research on my topic, but also use myself as a test subject and experience how the inclusion of the arts affected my life. Our project was successful in that we learned what we wanted to learn and we achieved our goals of immersing ourselves in the arts. Our goals were not meant to be too over the top, but more about learning through experiences and reporting on them. I learned a lot about my own way of learning new skills as well as developed a new outlook on how I value music as well as the arts in everyday life. I plan on continuing on playing the ukulele as well as trying other artistic activities such as drawing and writing over the summer because of the significant impact I saw while working on this project.
Wednesday, May 4, 2016
Your Brain Map
1. What do the frontal
lobes do?
2. What is the relationship between selective attention and learning?
Selective attention allows you to increase memory and allows you to select what is important. When learning, you select what is important to remember and how to use it.
3. What is the last part of your brain to develop and what can you do to prevent it from deteriorating?
It helps guide you by controlling motor skills.
2. What is the relationship between selective attention and learning?
Selective attention allows you to increase memory and allows you to select what is important. When learning, you select what is important to remember and how to use it.
3. What is the last part of your brain to develop and what can you do to prevent it from deteriorating?
The frontal is the last part to develop and you can prevent deterioration by being more active and connecting ideas that you learn to bigger ideas.
4. What does the neo cortex do?
4. What does the neo cortex do?
It helps guide you by controlling motor skills.
5. What is the role of the pre frontal cortex?
It controls your personality and how you act in social situations.
It controls your personality and how you act in social situations.
6. What do we know about the pre frontal cortex’s
relationship with multitasking?
It helps manage what is important and prioritizes one action over another.
It helps manage what is important and prioritizes one action over another.
7. Which part of the brain is associated with
speech and language development? Give an
interesting fact about this region.
The Broca's area helps with speech development. A person is still able to produce speech even when this area is damaged as functions shift to other parts.
The Broca's area helps with speech development. A person is still able to produce speech even when this area is damaged as functions shift to other parts.
8. Which part of your brain is responsible for
thinking the following: “Is it hot in here or is it just me?”
The Somatosensory cortex helps sense if the temperature is too cold or hot.
9. What does your visual cortex do for you?
The Somatosensory cortex helps sense if the temperature is too cold or hot.
9. What does your visual cortex do for you?
It helps differentiate color and identifies faces.
10. State three interesting or significant facts
about your occipital lobe.
It is the visual processing part of your brain. It allows you process long term and short term memories. You can exercise this part by using your imagination.
It is the visual processing part of your brain. It allows you process long term and short term memories. You can exercise this part by using your imagination.
11. What would happen if your temporal lobes were
damaged?
You will have trouble recalling things from memory.
You will have trouble recalling things from memory.
12. What is your “fast brain” and what does it do?
The fast brain is the motor cortex and helps control the senses
The fast brain is the motor cortex and helps control the senses
13. State 3 things that you could do that would
influence your synapses, and have a
positive affect on your life and health.
You can exercise and have a healthy diet as well as becoming an active learner
You can exercise and have a healthy diet as well as becoming an active learner
14.What is the relationship between multi-sensory
or multi-modal learning and your dendrites?
Multiple types of stimulation will help you learn things faster by engaging multiple parts of your brain
Multiple types of stimulation will help you learn things faster by engaging multiple parts of your brain
15.How does “big picture thinking” and mnemonics
affect dendrites and/or learning?
It helps by connecting ideas together and using your brain in different ways b actively learning
It helps by connecting ideas together and using your brain in different ways b actively learning
16. Describe a neurotransmitter
that you feel is very important. Justify
your reasoning.
I feel that dopamine is an important neurotransmitter because it helps you become motivated to do things and learn things.
I feel that dopamine is an important neurotransmitter because it helps you become motivated to do things and learn things.
17.What does the corpus callosum do?
it connects the two hemispheres. It controls oral skills and language and deals with handwriting as well as the movement of the eyes.
18. What is the relationship between music and the corpus callosum?
it connects the two hemispheres. It controls oral skills and language and deals with handwriting as well as the movement of the eyes.
The corpus collosum is strengthened through music as it strengthens communication between the two brains
19.Why is the thalamus
important?
The thalamus controls motor control and sensory imformation.
Relate and Review
In this activity I learned about the different parts of the brain. The simulation showed the relative areas that the parts covered and how they all fit together. The frontal lobe covered a large portion of the brain and it was interesting to learn how to keep the frontal lobe healthy with active learning. The neo cortex is a part of the brain that controls motor functions. The different neurotransmitters were also interesting to learn about and how each affected the brain and their function in everyday life. Healthy diets and exercise also help with dendrite health. The corpus collosum connects the two hemispheres of the brain and actually serves to help understand language and can be strengthened by practicing music.
Monday, May 2, 2016
Brain Dissection
1.
2. Brain stem- regulates automatic systems such as heart beat and breathing
Cerebellum- coordinates voluntary movement
Cerebrum- divided into four lobes and controls thought and action
Posterior- back part of the brain
Anterior- front part of the brain
3. Myelin helps impulses move across neurons faster
4.
5. Thalamus- controls information between cerebral cortex and lower brain helping with sesnory interpretation
Corpus Callosum- bridge between two hemispheres
Medulla Oblangota- controls heartbeat and breathing
Pons- controls information between cerebrum and cerebellum
Mid Brain- controls vision and hearing
Hypothalamus- helps control the endocrine system and hormone levels
Optic Nerve- transfers information from optic nerve to brain
6.
Relate and Review
In this lab we opened up a sheep brain and located the different parts of the brain. In this unit we learned about the parts of the brain ,and their functions. With the help of the clay model we did, this lab helped give us a better visual representation of what those parts look like ,and how they all fit together. This dissection helped us understand the shape and functions of each of the parts as well as gave us hands on experience.
Thursday, April 28, 2016
Sheep Eye Dissection Analysis
 The lens of the eye is used to focus on objects at various distances. Some of the vitreous humor is surrounding the lens. The vitreous humor helps refract light.
The lens of the eye is used to focus on objects at various distances. Some of the vitreous humor is surrounding the lens. The vitreous humor helps refract light. The opening is the pupil and the surrounding brownish layer is the iris. The pupil controls how much light enters the eye and the iris controls how big the pupil is The black layer is the ciliary body which helps stretch the lens in order to focus better on different objects.
The opening is the pupil and the surrounding brownish layer is the iris. The pupil controls how much light enters the eye and the iris controls how big the pupil is The black layer is the ciliary body which helps stretch the lens in order to focus better on different objects.
The transparent part is the cornea and the surrounding grey part is the sclera. The cornea allows light into the eye and helps with refraction and the sclera helps keep the shape of the eye ball.
The retina is the clear and thin gel layer and helps processes the image from the lens. The bluish and greenish part is the choroid. This part of the eye provides nourishment.
Thursday, April 14, 2016
The Clay Brain
In this activity we modeled the left hemisphere at the sagittal plane and the right cerebral hemisphere at the lateral view. The different parts are labeled and different colors were used to show the relative size and area of the part.
The Woman with a hole in her brain
A woman had trouble walking and felt nauseous. When she entered a hospital, it was discovered that she was missing cerebellum. The cerebellum controls voluntary movement as well as balance. It made sense that the woman felt these symptoms throughout her life, but it was miraculous that how minor they were. Her case shows how the brain how the brain can adapt and compensate for missing functions.
If the brain's Brocca's area is responsible for language and speech production. If someone were missing this area, they would not be able to produce speech. They could still survive without it and still be able to understand speech. The Wernicke's area can partially compensate by helping the person understand and process speech.
If the brain's Brocca's area is responsible for language and speech production. If someone were missing this area, they would not be able to produce speech. They could still survive without it and still be able to understand speech. The Wernicke's area can partially compensate by helping the person understand and process speech.
Thursday, March 24, 2016
Unit 7 Reflection
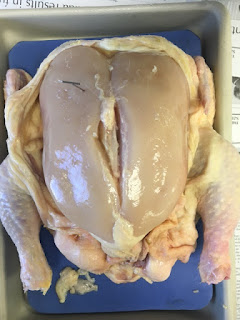
In this unit we learned about the different movements of the body and specific vocabulary to describe them. These movements happen at synovial joints. There are angular movements such as flexion and extension and special movements such as elevation and depression. We also learned about how muscles are organized and classified. Muscles are in charge of the movements of bones or fluids and help maintain posture and body posture. They have certain properties that help them with these functions i.e. contractility, extensibility, and elasticity. There are many terms that classify the size, shape, number of origins, and location of the muscles. These are used to identify specific types of muscles. To deepen our understanding we dissected a chicken carcass and identified the different muscles and tendons while relating them to human muscles. In this unit we also discussed how how muscles contract and how an impulse translates though to movement that is driven by the release of calcium and ATP. To illustrate this process, we made a muscle contraction video. To end the unit we went over how muscles develop ,and how specific types of exercises can help muscle health and growth. Muscles have slow twitch and fast twitch fibers. Long duration uses slow twitch while shorter duration exercises use fast twitch. Exercises such as weight lifting can benefit muscles while certain shortcuts can actually cause more harm such as steroids as shown by our satirical advertisement.
I enjoyed the different activities and labs in this unit because they helped simplify the complex system of muscles and how they worked. This unit made me more curious about how muscles develop ,and I want to learn more about how muscles are able to carry such large amounts of weight.
My New Year's goals are still in progress and I am currently doing well in staying more organized and being healthy. I feel that my lifestyle has changed ,and I am still working to make it better.
Chicken dissection
Advertisement that shows how the benefits of steroids do not outweigh the health problems that come with it
I enjoyed the different activities and labs in this unit because they helped simplify the complex system of muscles and how they worked. This unit made me more curious about how muscles develop ,and I want to learn more about how muscles are able to carry such large amounts of weight.
My New Year's goals are still in progress and I am currently doing well in staying more organized and being healthy. I feel that my lifestyle has changed ,and I am still working to make it better.
Wednesday, March 23, 2016
Performance Enhancements Advertisement
Steroids seem to appeal to people because they think that whatever they are currently doing is not enough for them to get the ideal body or meet their own standards. Anabolic steroids may increase muscle gain, but its costs are not worth it. It can cause an increase in blood pressure, heart disease, liver damage, stroke, and many other health problems. It can also affect gender specific qualities such as sperm count and breast size. Steroids are definitely not a safe performance enhancement.
Other enhancements such as high protein diets (if paired with the proper amount of exercise and done properly) and strength training are safe ways to increase performance and gain muscle. They might require more time the other ways, but have little to no risk if done properly as apposed to steroids and androstenedione which can cause an imbalance in hormones.
Tuesday, March 22, 2016
Chicken Muscle Dissection Analysis
1. In this lab we first obtained a chicken carcass and began identifying any muscles that we saw. To see more of the chest, we cut through the mid line and got a better look at the pectoralis major and pectoralis minor. After looking for any tendons and clumps of fat, we then opened up the back to locate the trapezius and latissmus dorsi. We then opened up the two different segments of the chicken wing to reveal the deltoid, biceps brachii, tricpes humeralis, flexor carpi ulnaris, and brachioradialis. In the last parts of the dissection we opened up the chicken's thigh and calf and located the various muscles in each part.
In relation to motion muscles play the role of producing motion by contracting and stabilizing body positions. Tendons attach muscle to bone and helps to move bone. The bone stabilizes the movement, so the limb stays in place. The biceps brachii contracts and bends the arm/ wing, causing movement. The humerus stabilizes the arm/wing and gives a platform for the muscle to move on.
The tendon at the origin stabilize the muscle and do not let it move while the tendon at the insertion allow the muscle to contract and move. At the origin it is broader while at the insertion it is narrower.
Muscles in chickens are similar in humans in that they both have similar functions. For example, they both have biceps brachii and triceps humeralis that help move the limb in a similar fashion. The bones also have similar structure with the chicken wing having a humerus, ulna, and radius. There also differences in that the muscles have different proportions than the human's muscles because the chicken's bodily structure is different.
2.
In relation to motion muscles play the role of producing motion by contracting and stabilizing body positions. Tendons attach muscle to bone and helps to move bone. The bone stabilizes the movement, so the limb stays in place. The biceps brachii contracts and bends the arm/ wing, causing movement. The humerus stabilizes the arm/wing and gives a platform for the muscle to move on.
The tendon at the origin stabilize the muscle and do not let it move while the tendon at the insertion allow the muscle to contract and move. At the origin it is broader while at the insertion it is narrower.
Muscles in chickens are similar in humans in that they both have similar functions. For example, they both have biceps brachii and triceps humeralis that help move the limb in a similar fashion. The bones also have similar structure with the chicken wing having a humerus, ulna, and radius. There also differences in that the muscles have different proportions than the human's muscles because the chicken's bodily structure is different.
2.
Monday, March 14, 2016
What happens when you stretch?
Relate and Review
When you stretch, you stretch certain fibers in your muscles. Proprioceptors perceive the movements of the muscles fibers and relay that information to the central nervous system. Muscle spindles record how far a muscle stretches, which results in stretch reflex that causes muscles to contract. There is an initial response called the static component and the dynamic component that only occurs moments after the stretch begins. Holding a stretch longer helps with muscle lengthening which occurs after the muscle relaxes after initially contracting. Reciprocal inhibition is when a muscle contracts and antagonist muscle is forced to relax. These factors that go into how muscles relax and contract when stretching can be applied to different exercises and gives me a new perspective as to why it is important to stretch for longer periods of time before working out.
"The dynamic component of the stretch reflex (which can be very powerful) lasts for only a moment and is in response to the initial sudden increase in muscle length."
This response is something I felt in class when I was first doing the stretch with my leg. At first I did not think my leg could go any further because of this response, but it was only the initial response
"Another reason for holding a stretch for a prolonged period of time is to allow this lengthening reaction to occur, thus helping the stretched muscles to relax. It is easier to stretch, or lengthen, a muscle when it is not trying to contract."
After multiple times contracting and relaxing my leg when it was being stretched I could feel it begin to relax more and more. It also became easier to stretch because the initial contraction faded away.
"You also want to relax any muscles used as synergists by the muscle you are trying to stretch. For example, when you stretch your calf, you want to contract the shin muscles (the antagonists of the calf) by flexing your foot."
This is an interesting idea that I never thought of before. By contracting certain muscles, other muscles relax and actually help you while stretching. I wonder what synergists are in play in different types of stretches.
When you stretch, you stretch certain fibers in your muscles. Proprioceptors perceive the movements of the muscles fibers and relay that information to the central nervous system. Muscle spindles record how far a muscle stretches, which results in stretch reflex that causes muscles to contract. There is an initial response called the static component and the dynamic component that only occurs moments after the stretch begins. Holding a stretch longer helps with muscle lengthening which occurs after the muscle relaxes after initially contracting. Reciprocal inhibition is when a muscle contracts and antagonist muscle is forced to relax. These factors that go into how muscles relax and contract when stretching can be applied to different exercises and gives me a new perspective as to why it is important to stretch for longer periods of time before working out.
"The dynamic component of the stretch reflex (which can be very powerful) lasts for only a moment and is in response to the initial sudden increase in muscle length."
This response is something I felt in class when I was first doing the stretch with my leg. At first I did not think my leg could go any further because of this response, but it was only the initial response
"Another reason for holding a stretch for a prolonged period of time is to allow this lengthening reaction to occur, thus helping the stretched muscles to relax. It is easier to stretch, or lengthen, a muscle when it is not trying to contract."
After multiple times contracting and relaxing my leg when it was being stretched I could feel it begin to relax more and more. It also became easier to stretch because the initial contraction faded away.
"You also want to relax any muscles used as synergists by the muscle you are trying to stretch. For example, when you stretch your calf, you want to contract the shin muscles (the antagonists of the calf) by flexing your foot."
This is an interesting idea that I never thought of before. By contracting certain muscles, other muscles relax and actually help you while stretching. I wonder what synergists are in play in different types of stretches.
Monday, February 29, 2016
Unit 6 Reflection
This unit focused primarily on the components of the skeletal system. This unit included topics such as the different functions of the bones as well as how the cells within the bones help with those functions as well as how bones repair themselves. The different cells, osteocytes, osteoblasts, and osteoclasts, work together to break bones and reform them in a process that is called bone remodeling. We also learned about the different types of bones and how their form fit their function in the skeletal system such as short bones, flat bones, and irregular bones. The disorders of the skeletal system taught us how bones can lose their density or shape and cause complications for our health. We also learned about the different classifications of bone fractures like complete fractures, fissure fractures, and comminuted fractures. After learning how bones can break in different ways, we learned how the bone repaired itself as well to show how the body responded to this type of damage by learning about each step in the process.
This unit made me more curious about how people can get hip or knee replacements and I wonder how that works in the body.
During this unit, I found that the more hands on labs were very helpful in understanding what the skeleton looked like. The owl pellet lab was especially helpful because it gave a sense of what the different skeleton parts looked like and it was a unique experience to relate the skeleton of the animal to that of a human. This unit I also kept toward my goals of being healthier in general by exercising more and sleeping more as well as staying more organized. I feel like I am making more progress with my lower stress.
This unit made me more curious about how people can get hip or knee replacements and I wonder how that works in the body.
During this unit, I found that the more hands on labs were very helpful in understanding what the skeleton looked like. The owl pellet lab was especially helpful because it gave a sense of what the different skeleton parts looked like and it was a unique experience to relate the skeleton of the animal to that of a human. This unit I also kept toward my goals of being healthier in general by exercising more and sleeping more as well as staying more organized. I feel like I am making more progress with my lower stress.
Thursday, February 25, 2016
Owl Pellet Lab
In this lab we dissected an owl pellet by locating bones and attempting to reconstruct the skeleton of the animal in the pellet. First we separated the fur from the bones and sorted them into similar piles. After finding as many bones as possible we then tried to reconstruct the skeleton using diagrams that were provided to us and at the same time attempting to identify the animal.
With the bones that we found we identified the animal as a rat. Our first source of evidence was the fur in the pellet which meant that the animal could not have been a bird. The shape of the front teeth, which were long,that were found on the skull also gave us clues that it was a rat. We used more identifiers from the packet given to us and saw even more evidence that the animal was a rat because of the shape and size of the skull, which was 3.0 cm long and 2.1 cm wide, as well as the more rounded shape of the molars. The skull was elongated and fit the size description. With all of these details and using process of elimination, we concluded that the animal was a rat.
The skeleton that we constructed had a few similarities to a human skeleton as you can see from the picture at the bottom. The skull like the human skull consisted of different plates and had the same basic features. There is also a similarity in the spine where the vertebrates are very similar in shape and make the spine in a similar way as the human spine with multiple vertebrate connecting to each other. There are also similarities between the rat's paws and the human's feet and hands. They have the same basic structure of the carpals, metacarpals, and carpals.
There are differences as well. The limbs of the rat have different proportions with the humerus being longer than the radius and the femur being longer than the tibia while the reverse is true in humans. The rat skeleton has a longer chain of vertebrate because of the tail while human vertebrates do not continue past the pelvis. A final difference is that even though the skull of the rat has the same basic features it is more elongated shape with the eye sockets being larger compared the eye sockets of the human skull.

With the bones that we found we identified the animal as a rat. Our first source of evidence was the fur in the pellet which meant that the animal could not have been a bird. The shape of the front teeth, which were long,that were found on the skull also gave us clues that it was a rat. We used more identifiers from the packet given to us and saw even more evidence that the animal was a rat because of the shape and size of the skull, which was 3.0 cm long and 2.1 cm wide, as well as the more rounded shape of the molars. The skull was elongated and fit the size description. With all of these details and using process of elimination, we concluded that the animal was a rat.
The skeleton that we constructed had a few similarities to a human skeleton as you can see from the picture at the bottom. The skull like the human skull consisted of different plates and had the same basic features. There is also a similarity in the spine where the vertebrates are very similar in shape and make the spine in a similar way as the human spine with multiple vertebrate connecting to each other. There are also similarities between the rat's paws and the human's feet and hands. They have the same basic structure of the carpals, metacarpals, and carpals.
There are differences as well. The limbs of the rat have different proportions with the humerus being longer than the radius and the femur being longer than the tibia while the reverse is true in humans. The rat skeleton has a longer chain of vertebrate because of the tail while human vertebrates do not continue past the pelvis. A final difference is that even though the skull of the rat has the same basic features it is more elongated shape with the eye sockets being larger compared the eye sockets of the human skull.
Thursday, January 28, 2016
Unit 5 Reflection
This unit focused on metabolism and the different types of the body's systems that affect it. We learned about subjects such as fuel metabolism by studying how the body uses certain molecules and biochemical pathways to meet energy demands. There are three main stages. The fed state is where food is being absorbed. The fasting state is when molecules are being broken down and stored. The starvation state is when the body starts using secondary energy supplies in order to keep functioning. We also discussed how metabolism could be disrupted by diabetes. Type 1 causes the immune system to attack beta cells and require people to take insulin shots. Type 2 begins as insulin resistance and leads to the body not being able to respond properly to insulin at all. The endocrine system controls processes that are involved in equilibrium with the use of hormones, which are controlled by specialized organs. The lymphatic system's purpose is for lipid absorption, immunity, and fluid recovery. The lymph flows like blood with the use of lymph vessels.
During this unit, I felt like I was able to learn a lot of different subjects that I could apply to me own life, but I still need to work on my active learning because I am not retaining as much information I should be.
I really enjoyed the activity of creating the model of the digestive system because it helped me visualize how long it was ,and how the different parts compared to each other.
http://ezanatandphys.blogspot.com/2016/01/digestive-system-lab-questions.html
I also enjoyed the readings and the different articles we had to read about metabolism because it gave me a more real world and in depth perspective on what we were learning in class.
For this unit, I still want to learn more about how different foods can affect metabolism and still wonder how age can affect it.
I have been working on my new year goal of being healthier by sleeping more than I used to and by exercising more consistently, but for my other goal I still need to work on keeping up with my classes and staying organized.


Posters to review stages of metabolism and the organs and hormones associated with them.
During this unit, I felt like I was able to learn a lot of different subjects that I could apply to me own life, but I still need to work on my active learning because I am not retaining as much information I should be.
I really enjoyed the activity of creating the model of the digestive system because it helped me visualize how long it was ,and how the different parts compared to each other.
http://ezanatandphys.blogspot.com/2016/01/digestive-system-lab-questions.html
I also enjoyed the readings and the different articles we had to read about metabolism because it gave me a more real world and in depth perspective on what we were learning in class.
For this unit, I still want to learn more about how different foods can affect metabolism and still wonder how age can affect it.
I have been working on my new year goal of being healthier by sleeping more than I used to and by exercising more consistently, but for my other goal I still need to work on keeping up with my classes and staying organized.


Posters to review stages of metabolism and the organs and hormones associated with them.
Wednesday, January 6, 2016
Digestive System Lab Questions
1. In this lab the length of the parts of the digestive system were estimated by using different lengths that could be measured outside of the body. Using these lengths and different color string, we created a model of our own digestive systems. It helped us visualize the length of each part and the entire digestive system.
Digestive Organ
|
Color and Length(cm)
|
Mouth
|
blue 13 cm
|
Esophagus
|
red 52.3 cm
|
Stomach
|
green 19 cm
|
Small Intestine
|
711.2 cm
|
Large Intestine
|
blue 177.8 cm
|
Total
|
973.3 cm
|
2. My digestive system is about 5.5 times longer than my height. It is able to fit inside my abdomen because it is folded multiple times, so it takes up less space.
3. I predict that it takes about 12 hours for food to move through the entire digestive system. The actual number is about 24 hours. Factors that affect this time is what is being digested ,and the health of the person.
4. Digestion is basically breaking down food into smaller parts. Organs that help with digestion are the mouth, saliva glands, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, pancreas, liver, and gall bladder. Organs that help with absorption, which is how nutrients are taken from food, are the small intestine and large intestine.
5. I still want to learn how different types of foods are treated by the digestive system.
Monday, January 4, 2016
New Year's Goals
This semester I will put in the effort to be healthier. Because I am a second semester senior, there is less pressure to get high grades, so I will have the opportunity to live a healthier life style. While getting consistent exercise, I will keep track of the type of foods I eat and make sure that I get enough sleep. This means that I will make sure to manage my time better in order to weed out any type of procrastination that will cause me to sleep past midnight. I will make sure to get the same amount of sleep every night.
For this class another goal I have is to make sure I become a more active learner. This means not only listening in class and doing the assignments but also reviewing what I learn each day and taking the time to connect what I learn in class to things outside of class. I will take the time to read through the notes and make flash cards of concepts that I have a hard time grasping. This type of learning will help me actually learn and retain material while getting more out of the class. Active learning will also help during nights before the test which usually meant a night of desperate cramming, but because I will have retained the information I needed I won't have to stay up late studying. With this type of learning I will gain a deeper understanding of the material in class.
For this class another goal I have is to make sure I become a more active learner. This means not only listening in class and doing the assignments but also reviewing what I learn each day and taking the time to connect what I learn in class to things outside of class. I will take the time to read through the notes and make flash cards of concepts that I have a hard time grasping. This type of learning will help me actually learn and retain material while getting more out of the class. Active learning will also help during nights before the test which usually meant a night of desperate cramming, but because I will have retained the information I needed I won't have to stay up late studying. With this type of learning I will gain a deeper understanding of the material in class.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)