1. In this lab we first obtained a chicken carcass and began identifying any muscles that we saw. To see more of the chest, we cut through the mid line and got a better look at the pectoralis major and pectoralis minor. After looking for any tendons and clumps of fat, we then opened up the back to locate the trapezius and latissmus dorsi. We then opened up the two different segments of the chicken wing to reveal the deltoid, biceps brachii, tricpes humeralis, flexor carpi ulnaris, and brachioradialis. In the last parts of the dissection we opened up the chicken's thigh and calf and located the various muscles in each part.
In relation to motion muscles play the role of producing motion by contracting and stabilizing body positions. Tendons attach muscle to bone and helps to move bone. The bone stabilizes the movement, so the limb stays in place. The biceps brachii contracts and bends the arm/ wing, causing movement. The humerus stabilizes the arm/wing and gives a platform for the muscle to move on.
The tendon at the origin stabilize the muscle and do not let it move while the tendon at the insertion allow the muscle to contract and move. At the origin it is broader while at the insertion it is narrower.
Muscles in chickens are similar in humans in that they both have similar functions. For example, they both have biceps brachii and triceps humeralis that help move the limb in a similar fashion. The bones also have similar structure with the chicken wing having a humerus, ulna, and radius. There also differences in that the muscles have different proportions than the human's muscles because the chicken's bodily structure is different.
2.

Sartorius-flexes thigh and runs across front of the thigh

Latissimus dorsi- extend or pull wing/arm

Trapezius- run perpendicular from backbone to shoulders

Iliotibialis- extends the thigh and flexes the leg

Deltoid- helps raise arm/wing

Biceps brachii-flexes arm/wing

Quadriceps- group of four muscles,extends lower leg

Gastrocnemius-primary muscle of the dorsal and medial sides of drumstick

Brachioradialis- largest muscle on the superior side of the lower wing
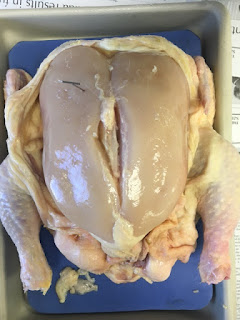
Pectoralis major- pull wings ventrally

Latissimus dorsi- extend or pull wing/arm

Peroneus longus-

Triceps humeralis- extends and straightens wing/arm

Peroneus longus- extends foot

Flexor carpi ulnaris- flexes hand, runs from back to elbow to side of hand

Pectoralis minor- pulls shoulder down and forward

Tibialis anterior- flexes the foot





















