Stem cells are similar to any other eukaryotic cells found in the body and have the same types of organelles. As this article states, in adults they are found in bone marrow or fat and in developing embryos, playing a key role in the early development of animals and humans.
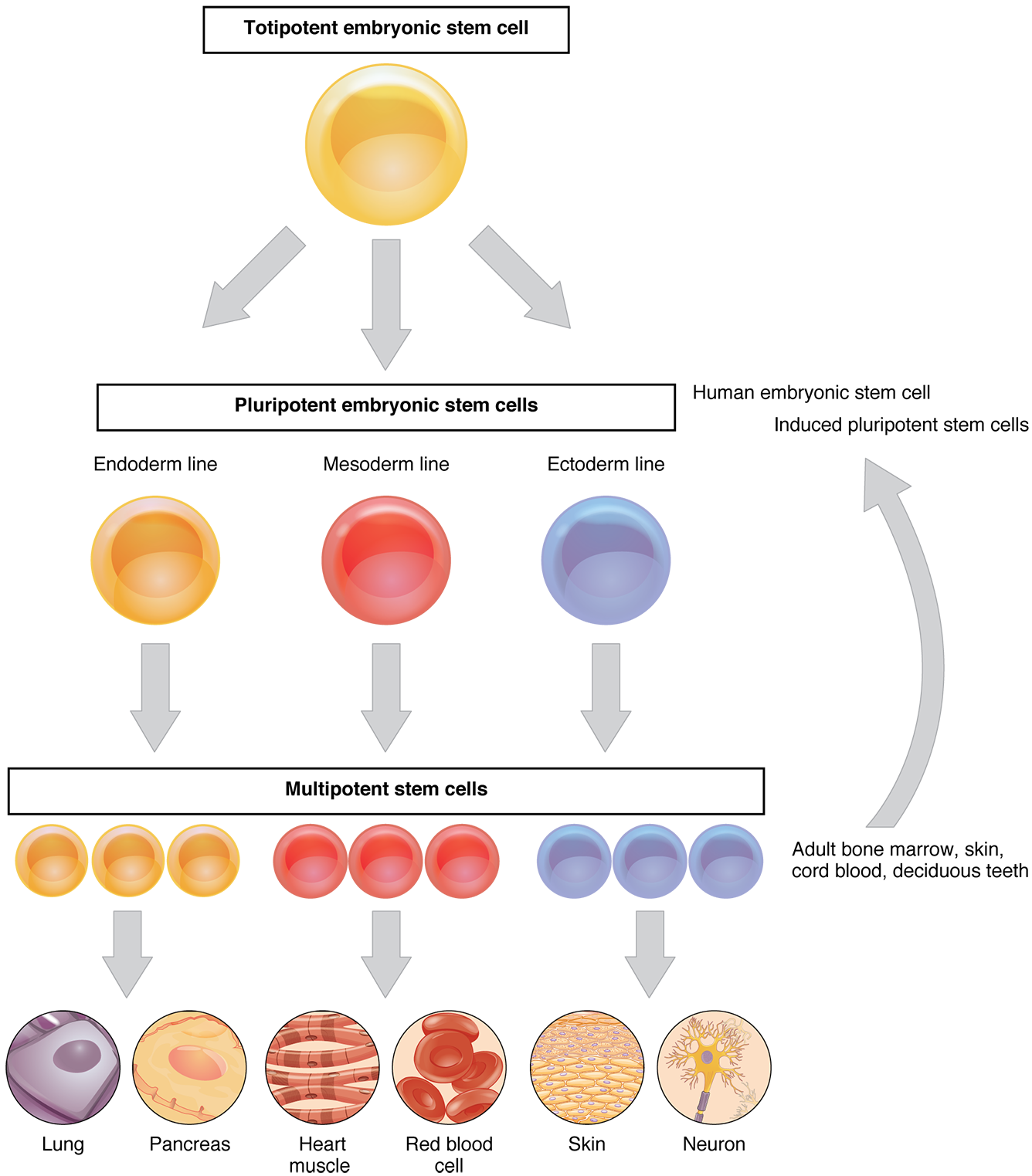
These cells are known as specialized cells and divide when the body needs new cells. According to the National Institute of Health, they are the body's internal repair system. They can specialize themselves and become another type of cell. They can become tissue cells, blood cells, brain cells, and many other types of cells depending on what the body needs. For example when the body is damaged and a muscle cell needs to be replaced, stem cells can reprogram themselves and become specialized muscle cells to replace those that were lost. According to this article, in embryos of developing humans stem cells are essential to the development of the vital organs and the different body parts. The ability of stem cells to self renew and the flexibility in its development play a vital role in disease research.
Because the stem cell is unspecialized, it cannot be categorized into any of the tissue types because it can actually become any of them. They can become muscle cells, connective tissue, nerve cells, and any other cell that the body needs.
Human Embryonic Cells